MEDICINE BLENDED ASSAIGNMENT
https://amishajaiswal03eloggm.
1A)Myelopathy hand-loss of power of adduction and extension of ulnar two or three finger and an inability to grip and release rapidly with these fingers .These changes are termed as 'myelopathy hand' it is due to pyramidal tract involvement.
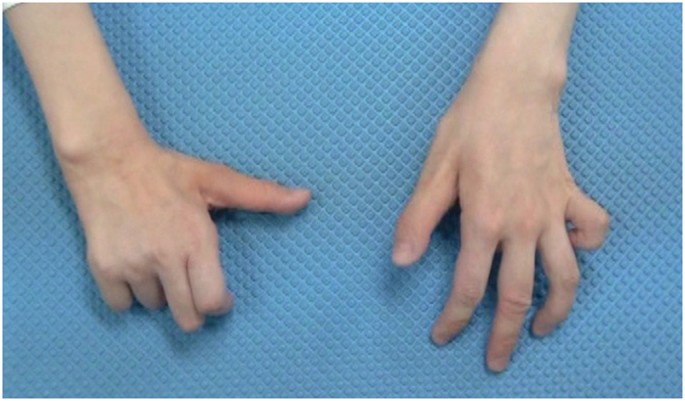
2a)it is also known as Wartenberg sign is a neurological sigh of involuntary abduction of little finger caused by unopposed action extensor digiti minimi .It is seen in cervical myelopathy.
3A)Hoffman reflex -it is a neurological examination finding elicited by reflex test which can help to verify the presence or absence of issue arising from corticospinal tract.

http://
1A)Yes, the history of RTA may play role in present condition . Which may be the cause for infract in left middle cranial artery territory. Which led to decrease supply to left internal capsule, caudate, putamen, left thalamus, left insular lobe.
2A) 1.Sudden onset of weakness or numbness on one side of body. 2.sudden speech difficulty or confusion. 3.sudden difficult in seeing in one or both eye. 4.sudden severe headache. 5.loss of balance, difficulty in walking, dizziness.
3A)tissue plasminogen activator- alteplase, tenecteplase- break down of clot mannitol-to lower ICP aspirin-COX inhibitor-to make blood thin atovarstatin-decrease LDL and increase HDL
4A)Alcohol consumption has no role in development of CVA as patient consume alcohol occasionally .
5A)HDL-absorb cholesterol and carry back to liver where the liver flushes out cholesterol from body . high level of HDL decrease the risk of heart diseases.
https://nehae-logs.blogspot.
1A)pleural effusion might be the cause of dyspnea. relation of effusion and pancreatitis:
increase permeability of lymphatics may lead to shift of pancreatic enzymes from abdomen to thorax. impairment of drainage of pleural exudate caused by lymphatic obstruction. increase in permeability of diaphragm lead to inflammation of adjacent pancreas.
2A)hyperglycemia may be caused due to decrease synthesis of insulin which is damage of beeta cells of pancreas in acute pancreatitis.
3A)LFT is elevated due to HEPATIC CELL DAMAGE if there is liver damage there is increase level ALT level in our body *ALT and AST are specific marker for Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
4a)Plan of action and Treatment:
Investigations:
✓ 24 hour urinary protein
✓ Fasting and Post prandial Blood glucose
✓ HbA1c
✓ USG guided pleural tapping
Treatment:
• IVF: 125 mL/hr
• Inj PAN 40mg i.v OD
• Inj ZOFER 4mg i.v sos
• Inj Tramadol 1 amp in 100 mL NS, i.v sos
• Tab Dolo 650mg sos
• GRBS charting 6th hourly
• BP charting 8th hourly
https://chennabhavana.
1a)HEMOPERITONIUM might be the probable diagnosis
2A)In hemoperitonium the blood accumulate in various abdominal cavities . which lead to decrease perfusion to various organs which lead to shock and finally death.
3a)NSAIDS intake for long duration may lead to drug induced hepatitis
https://kavyasamudrala.
1A)cause of SOB-METABOLIC ACIDOSIS metabolic acidosis in kidney disease may lead to: *impaired ammonia excretion * reduced tubular bicarbonate reabsorption * insufficient renal bicarbonate production
2A)metabolic acidosis cause fatigue by inhibition of release of ca+2 from SR which decrease the activity of muscle contraction.
3a)the cause of fleshy mass in urine might be due to papillary necrosis following hydronephrosis
4a)after TURP surgery there might be urethral stenosis which cause backflow of urine which lead Hydronephrosis and to papillary necrosis.
https://drsaranyaroshni.
3a) Evaluation and Treatment of ADHD in Children and Adolescents*

https://vyshnavikonakalla.
The most effective prevention of IRIS would involve initiation of ART before the development of advanced immunosuppression. IRIS is uncommon in individuals who initiate antiretroviral treatment with a CD4+ T-cell count greater than 100 cells/uL.
Aggressive efforts should be made to detect asymptomatic mycobacterial or cryptococcal disease prior to the initiation of ART, especially in areas endemic for these pathogens and with CD4 T-cell counts less than 100 cells/uL.
Two prospective randomized studies are evaluating prednisone and meloxicam for the prevention of paradoxical TB IRIS.
https://kavyasamudrala.
Presence of a left-lobe abscess more than 10 cm in diameter
Impending rupture and abscess that does not respond to medical therapy within 3-5 days.
- Stage 1 -- Mild -- FEV-1 ≥80%: You may have no symptoms. You might be short of breath when walking fast on level ground or climbing a slight hill.
- Stage 2 -- Moderate -- FEV-1 50-79%: If you’re walking on level ground, you might have to stop every few minutes to catch your breath.
- Stage 3 -- Severe -- FEV-1 30-49%: You may be too short of breath to leave the house. You might get breathless doing something as simple as dressing and undressing.
- Stage 4 -- Very Severe -- FEV-1 ≤30%: You might have lung or heart failure. This can make it hard to catch your breath even when you’re resting. You might hear this called end-stage COPD.
- anatomical localization of disease in patient is BRONCHIOLE
- Primary etiology of COPD in this patient is exposure to PADDY FOR LONG DURATION.
2a)Treatment
- Quitting smoking
The most essential step in any treatment plan for COPD is to quit all smoking. Stopping smoking can keep COPD from getting worse and reducing your ability to breathe. Bronchodilator
Bronchodilators are medications that usually come in inhalers — they relax the muscles around your airways. This can help relieve coughing and shortness of breath and make breathing easier. xamples of short-acting bronchodilators include:
- Albuterol (ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA, others)
- Ipratropium (Atrovent HFA)
- Levalbuterol (Xopenex)
Examples of long-acting bronchodilators include:
- Aclidinium (Tudorza Pressair)
- Arformoterol (Brovana)
- Formoterol (Perforomist)
- Indacaterol (Arcapta Neoinhaler)
- Tiotropium (Spiriva)
- Salmeterol (Serevent)
- Umeclidinium (Incruse Ellipta)
Inhaled steroids
Inhaled corticosteroid medications can reduce airway inflammation and help prevent exacerbations. Side effects may include bruising, oral infections and hoarseness. These medications are useful for people with frequent exacerbations of COPD. Examples of inhaled steroids include:
- Fluticasone (Flovent HFA)
- Budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler)
Combination inhalers
Some medications combine bronchodilators and inhaled steroids. Examples of these combination inhalers include:
- Fluticasone and vilanterol (Breo Ellipta)
- Fluticasone, umeclidinium and vilanterol (Trelegy Ellipta)
- Formoterol and budesonide (Symbicort)
- Salmeterol and fluticasone (Advair HFA, AirDuo Digihaler, others)
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors
A medication approved for people with severe COPD and symptoms of chronic bronchitis is roflumilast (Daliresp), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor. This drug decreases airway inflammation and relaxes the airways. Common side effects include diarrhea and weight loss.
Antibiotics
Respiratory infections, such as acute bronchitis, pneumonia and influenza, can aggravate COPD symptoms. Antibiotics help treat episodes of worsening COPD, but they aren't generally recommended for prevention. Some studies show that certain antibiotics, such as azithromycin (Zithromax), prevent episodes of worsening COPD, but side effects and antibiotic resistance may limit their use.
3a)cause of acute exacerbation might be upper respiratory tract infection and allergen exposure(paddy)
4a)ATT could have effected the patient’s condition by causing generalised weakness.
5a) Hyponatremia in patients with COPD developed secondary to many reasons, such as development or worsening of hypoxia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, and right-side heart failure with development of lower limb edema, renal insufficiency, use of diuretics, Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Synthesis, malnutrition, and poor intake during acute exacerbations are common contributing factors in such patients . Moreover, respiratory acidosis with metabolic alkalosis (owing to renal compensation) in patients with COPD with chronic hypercapnia is the usual cause of hypochloremia in those patients. So, patients with severe COPD exacerbation have factors that influence serum electrolytes levels like hypoxia, respiratory acidosis, and hypervolemia, even before starting any type of treatment that may further cause electrolyte imbalance
- history of giddiness 7 days back. It started at around 7 am when the patient was doing his usual morning routine. He suddenly felt giddy and took rest, after which it subsided briefly. This was associated with 1 episode of vomiting on the same day.
- - Patient was asymptomatic for 3 days, after which he consumed a small amount of alcohol.
- - He then developed giddiness, that was sudden in onset, continuous and gradually progressive. It increased in severity upon getting up from the bed and while walking.
- - This was associated with Bilateral Hearing loss, aural fullness and presence of tinnitus.
- - He has associated vomiting- 2-3 episodes per day, non projectile, non bilious containing food particles.
- - Patient has H/o postural instability- he is unable to walk without presence of supports, swaying is present and he has tendency to fall while walking
- anatomical localization is CEREBRAL BLOOD VESSELS
- DENOVO HTN is primary etiology of this problem.
2a)PHARMACOLOGICAL INNTERVENTIONS
1)Tab Veratin
MECHANISM:
Betahistine is one of the few drugs known which is said to improve the microcirculation of the inner ear. It works as a histamine analogue through 2 modes of action
(1) agonist of H1 receptors and
(2) antagonist of H3 receptors.
It has a weak effect on H1 receptors but strong effect on H3 receptors.
2)Inj Zofer
MECHANISM:
Zofer Tablet works by inhibiting the action of a chemical substance named serotonin, which is responsible for inducing nausea and vomiting. Ondansetron binds to a receptor known as 5-HT₃, thus inhibits the binding of serotonin to it and prevents vomiting and nausea.
3)Tab Ecosprin
MECHANISM:
Ecosprin is an antiplatelet medicine. It works by inhibiting the action of an enzyme, which makes platelets aggregate together to form a blood clot.
4)Tab Atorvostatin
MECHANISM:
Atorvastatin is in a class of medications called HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins). It works by slowing the production of cholesterol in the body to decrease the amount of cholesterol that may build up on the walls of the arteries and block blood flow to the heart, brain, and other parts of the body.
5)Tab Clopidogrel
MECHANISM:
The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP- mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible.
6)Inj Thiamine
MECHANISM:
Thiamine combines with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the liver, kidneys, and leukocytes to produce thiamine diphosphate. Thiamine diphosphate acts as a coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism, in transketolation reactions, and in the utilization of hexose in the hexose-monophosphate shunt.
https://63konakanchihyndavi.
* Since we cannot take risk , we should however administer antibiotics also ( like in pyogenic liver abcess)
Zostum is a combination of drugs - SULBACTUM (pencillin) & CEFOPERAZONE(cephalosporin) [Antibiotic]: It is used here to treat if any bacterial cause ( since we can’t take the risk relying on only anti amoebic therapy)
* INJECTION. METROGYL 500mg IV TID ( thrice daily )
Metrogyl has the drug called METRONIDAZOLE [Antibiotic]: For amoebic cause
* INJECTION. OPTINEURIN 1amp in 100 ml NS( Nor
mal Saline) IV OD ( once daily)
Optineurin is a multivitamin drug { A combination of B1,B2, B3, B5,B6, B12 } given here as a supplement
* TAB. ULTRACET 1/2 QID( four times a day)
Ultracet is a combination of drugs - TRAMADOL(opiod analgesic) and ACETAMINOPHEN (analgesic and antipyretic) : Given for pain and fever
* TAB. DOLO 650 mg SOS (if needed) given for fever and pain
* Here ; due to medical therapy his symptoms subsided and clearly we can see it in usg reports ( liquefaction) meaning abcess responded to our medical therapy.
*And the patient was discharged on 10/5/21.
* We donot aspirate the pus since it is self resolving and aspiration is associated with several other complications.
* However there are some important indications for draining the abcess often asked in exams.
4a)diagnosis of pyogenic liver abscess
- an abdominal ultrasound to locate an abscess
- a CT scan with intravenous contrast, or injected dye, to find and measure the abscess
- blood tests to look for signs of infectious inflammation, such as an increased serum white blood count and neutrophil level
- blood cultures for bacterial growth to determine which antibiotic(s) you need an MRI of the abdomen
http://manikaraovinay.
Anatomical localisation : Medial canthus of left , Oral cavity and hardpalate, left nasal cavity and left frontal & temporal lobes
etiology: as the patient is diagnosed to have DKA poor control of sugar level in body led to development of mucormycosis.
https://kattekolasathwik.
https://63konakanchihyndavi.
abdominal pain in umbilical, left hypochondriac, left lumbar and hypogastric regions.
* Abdominal pain was incresed after food intake.
//
* Pain is throbbing type and radiating to back and is associated with nausea and vomiting( 1 episode) , which is non bilious, non projectile and also has food particles and water content 1 week.
//
* Fever was high grade, continuous and associated with chills and rigors.
//
Then he developed constipation since 4 days and passing flatus.
//
* patient also had burning micturition since 4 days, which is associated with suprapubic pain, increased frequency and urgency
anatomical localization of pain:abdominal pain in umbilical, left hypochondriac, left lumbar and hypogastric region
alcohol consumption is the primary etiology of patient problem.
2a)TREATMENT ALONG WITH RATIONALE
1) ING. MEROPENAM ; TID for 7 days
2) ING. METROGYL 500 mg IV TID for 5 days
* inj. Metrogyl has METRONIDAZOLE
( Nitroimidazole drug ) an antibiotic
3) ING. AMIKACIN 500 mg IV BD for 5days
* It is an Aminoglycoside antibiotic
## Here all three of these (Inj. Meropenem, Inj. Metrogyl, Inj. Amikacin ) are used as antibiotics to control infection and ; to prevent septic complications of acute pancreatitis.
4) TPN ( Total Parenteral Nutrition )
* Method of feeding that by passes gastrointestinal tract
* Fluids are given to vein , it provides most of the nutrients body needs.
* TPN has proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
5) IV NS / RL at the rate 12l ml per hour
* Given for fluid replacement ie., treat dehydration
6) ING. OCTREOTIDE 100 mg SC , BD
* It is a Somatostatin long acting analogue.
* It is used here to decrease exocrine secretion of pancreas and it also has anti- inflammatory & cytoprotective effects.
7) ING. PANTOP 40 mg IV , OD
* Inj. Pantop has PANTOPRAZOLE ( Proton Pump Inhibitor) used for its anti pancreatic secretory effect.
8) ING. THIAMINE 100 mg in 100 ml NS IV , TID
* It is B1 supplement.
* It is given here because; due to long fasting & TPN usage , body may develop B1 deficiency
* Wernicke encephalopathy secondary to B1 deficiency may be caused... so a prophylactic B1 supplemention is necessary.
9) ING. TRAMADOL in 100 ml NS IV , OD
* It is an opioid analgesic, given to releive pain.
https://muskaangoyal.blogspot.
- Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) – also referred to as diastolic heart failure. The heart muscle contracts normally but the ventricles do not relax as they should during ventricular filling (or when the ventricles relax).
- Reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) – also referred to as systolic heart failure. The heart muscle does not contract effectively, and therefore less oxygen-rich blood is pumped out to the body.
https://preityarlagadda.
mechanism: Through its action in antagonizing the effect of aldosterone, spironolactone inhibits the exchange of sodium for potassium in the distal renal tubule and helps to prevent potassium loss.
2. TAB. Acitrom
mechanism: Acenocoumarol inhibits the action of an enzyme Vitamin K-epoxide reductase which is required for regeneration and maintaining levels of vitamin K required for blood clotting
3. TAB. Cardivas
mechanism:Carvedilol works by blocking the action of certain natural substances in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels. This effect lowers your heart rate, blood pressure, and strain on your heart. Carvedilol belongs to a class of drugs known as alpha and beta-blockers.
4. INJ. HAI S/C
MECHANISM:Regulates glucose metabolism
Insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis; targets include skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue
5.TAB. Digoxin
mechanism:
Digoxin has two principal mechanisms of action which are selectively employed depending on the indication:
Positive Ionotropic: It increases the force of contraction of the heart by reversibly inhibiting the activity of the myocardial Na-K ATPase pump,
an enzyme that controls the movement of ions into the heart
6. Hypoglycemia symptoms explained
7. Watch for any bleeding manifestations like Petechiae, Bleeding gums.
8. APTT and INR are ordered on a regular basis when a person is taking the anticoagulant drug warfarin to make sure that the drug is producing the desired effect.
https://
- She had H/O heartburn like episodes since a year. They were relived without use of any medication.
- She has H/O TB diagnosed 7 months ago for which she completed the course of medication a month ago.
- Patient was apparently asymptomatic till 9pm on that day (27/4/21). She apparently ate dinner and slept. When she woke up at night for washroom she developed sweating on exertion and shortness of breath even at rest.
- came to the OPD with C/O shortness of breath (SOB) since 1/2 hour.
| Therapy | Recommendations for STEMI |
|---|---|
| Atorvastatin (Lipitor) | 40 to 80 mg per day |
| Morphine | 4 to 8 mg IV every five to 15 minutes as needed |
| Nitroglycerin | 0.4 mg sublingually every five minutes, up to three doses as blood pressure allows |
| 10 mcg per minute IV |
4A)Complications can include:
- Injury to the heart arteries, including tears or rupture
- Infection, bleeding, or bruising at the catheter site
- Allergic reaction to the dye or contrast used
- Kidney damage from the dye or contrast
- Blood clots that can lead to stroke or heart attack
- Bleeding into the abdomen (retroperitoneal bleeding)
TAB. ASPIRIN 325 mg PO/STAT- COX inhibitor prevent clot formation
TAB ATORVAS 80mg PO/STAT-atorvastatin reduce LDL and increase HDL
TAB CLOPIBB 300mg PO/STAT-DRUGS GIVEN: The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP- mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible.
INJ HAI 6U/IV STAT- insulin which help in uptake of glucose using GLUT2 receptor in cardiac tissue, muscle and adipose tissue










Comments
Post a Comment